Thelephora
punicea Alb.
& Schwein. 1805
Syn.: Tomentella punicea (Alb. & Schwein.) J. Schrφt. 1888
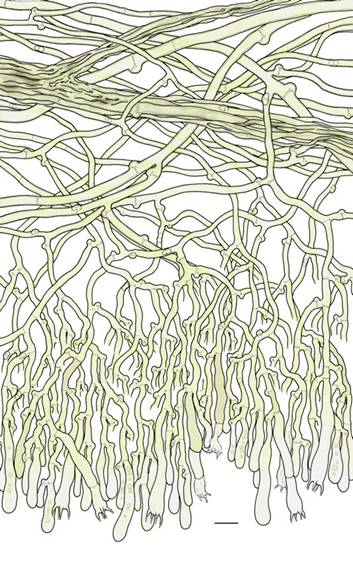
Basidiome effused, adherent to separable, at first araneose then hypochnoid to pellicular, soft to membranaceous;
up to 0.5 (1) mm thick.
Hymenophore granulose to finely colliculose,
smoother toward the margin, becoming partly crustose when old; with small dark
reddish brown droplets on surface when actively growing.
Colliculi (when developed) 38/mm, 0.10.2 mm across, more or less
easily peeled off from the subiculum, single to crowded.
Hymenial surface soon continuous, yellowish brown (10YR 54/46), ferrugineous brown (5YR 4(3)/46), frequently with an olivaceous hue (2.55Y 54/46); sometimes with very dark
brown spots.
Subiculum thin to well developed, hypochnoid
to fibrous, yellowish-brown to brown or strong brown (10YR 54/48).
Margin indistinct or narrow, shortly or widely thinning out, araneose, byssoid to fimbriate,
sometimes fan-shaped, yellowish-brown to brown, paler to concolour
with the subiculum.
Rhizomorphs present, sometimes obscure, common at the margin, in
subiculum and in cracks of the substrate, up to 0.1 (0.2) mm thick, compact,
becoming hard and rigid, with almost smooth surface, brownish to very dark
brown or almost blackish.
Hyphal system dimitic with branched skeletal hyphae (binding-like)
associated with rhizomorphs.
Subicular hyphae regular, mostly fibulate,
sometimes with simple septa and repetitive adventitious septa, mostly with thin
or slightly thickening wall, 24 (5) ΅m in diam., subhyaline
to yellowish brown or olivaceous.
Subhymenial hyphae regular, fibulate,
(2) 34 (5) ΅m wide, thin-walled, hyaline to pale yellowish, sometimes with
articles with homogeneous yellowish-ochraceous
content.
Rhizomorphs starting as thin strands of generative hyphae like the subicular ones showing soon slightly thicker walls and
alternating clamped and simple septa, then developing in the core of the rhizomorph
slightly wider hyphae up to 8 ΅m in diam., often with repetitive secondary
septa, and in surface mixed with thinner skeletoid
hyphae (1) 1.52.5 (3) ΅m diam., irregular, sinuous, often with elbow-like
bends that become randomly branched, ochre-brown to olivaceous,
never forming a labyrinthic and compact structure.
Cystidia absent.
Basidia narrowly clavate to subcylindrical, somewhat sinuous, (35) 4050 (60) x 68 ΅m,
sometimes or often with a transverse septum, fibulate
at the basal septum, subhyaline to pale yellowish,
sometimes with homogeneous light ochraceous content,
often with distinct yellowish oily drops; 4 sterigmata
up to 5 ΅m long and 11.5 ΅m wide at the base.
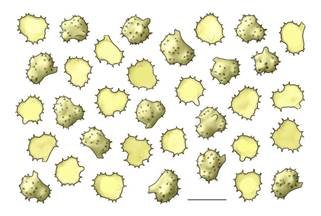
Basidiospores with irregular to lobed outline;
in frontal view normally 3-lobed, in lateral view mostly 2-lobed and often
broader toward the base, in polar view subglobose with irregular or slightly
lobed outline, (6) 6.58.5 (9) x (4.5) 56 .5 (7) x (6) 6.57.5 (8) ΅m, Q1
= 1.21.4 (1.5), Q2 = 0.951.2, echinulate, thick-walled, yellowish
to yellowish-brown; aculei up to 1 (1.2) ΅m long,
blunt to tapering, sometimes disposed in crowns over secondary lobes; apiculus
prominent.
Chlamydospores absent.
Incrustation: with a lot of yellow to yellowish-brown, rarely brown
resinous material that almost completely dissolve in KOH-mounts producing a
yellowish or yellowish brown diffusate.
Chemical reactions: IKI . CB: young basidiospores
slightly cyanophilous. KOH: faint pH-related color change of tissues that loss some yellow hue becoming
slightly more olivaceous brown; rhizomorphs becoming olivaceous or greenish, tipically
with more or less indefinite dark to very dark greenish areas or spots.
description: Elia Martini

drawings: Elia Martini